Sole is a fish belonging to several families. Generally
speaking, they are members of the family Soleidae, but, outside Europe, the
name sole is also applied to various other similar flatfish, especially other
members of the sole suborder Soleoidei as well as members of the flounder
family. In European cookery, there are several species which may be considered
true soles, but the common or Dover sole Solea solea, often simply called the
sole, is the most esteemed and most widely available.
Sole, any of a variety of flatfishes, but, more strictly,
those of the family Soleidae (order Pleuronectiformes).
Soles in this
restricted sense constitute about 30 genera and 130 species of flatfishes found
in temperate and tropical seas. Like numerous other flatfishes, soles are
flattened, more or less elongated fishes, with both small eyes on the right
side of the head.
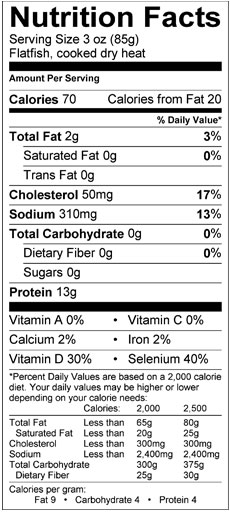
Flatfish are all low fat white fish with a mild taste. The
taste and texture varies from one species to another. All flatfish are less
than 100 calories per 3 ounce cooked serving, are a good source of protein and
have less than 2 grams of fat. Most flatfish species are also a good source of
niacin, B vitamins, phosphorus, calcium and selenium
Nutritional Facts